One day, you will need to monitor your database to analyse the performences, the number of queries, … Some tools exist !
pg_top
This is the cousin of the simple commant top, but applied to psql. It will show you the active connection.
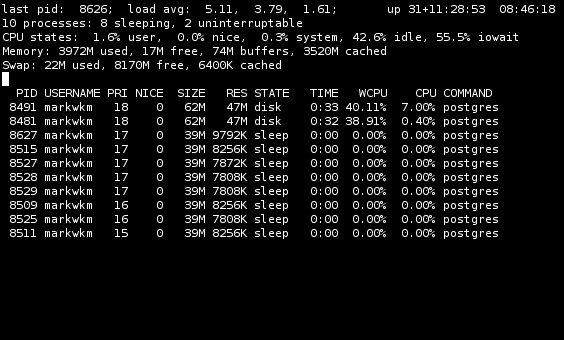
See the process list
This is the default screen. To start pg_top:
pg_top [-d ] [-U ] [-W]
Where ‘-d’ specifies the database to connect to, ‘-U’ specifies the database user, and ‘-W’ will prompt for the password if a password is required to connect.
Current query
Use the ‘Q’ key and enter a PID once pg_top is started.
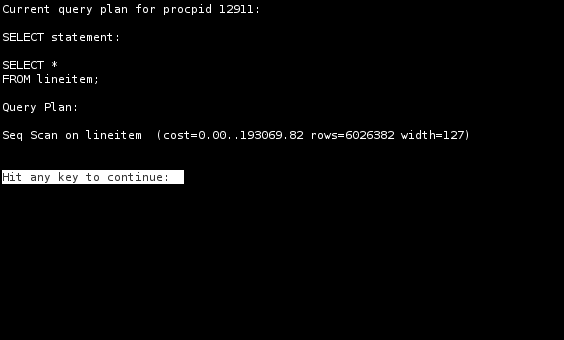
Query plan
Use the ‘E’ key and enter a PID once pg_top is started. The ‘E’ commands runs ‘EXPLAIN’ and ‘EXPLAIN ANALYZE’ can be used by using the ‘A’ key followed by a PID.
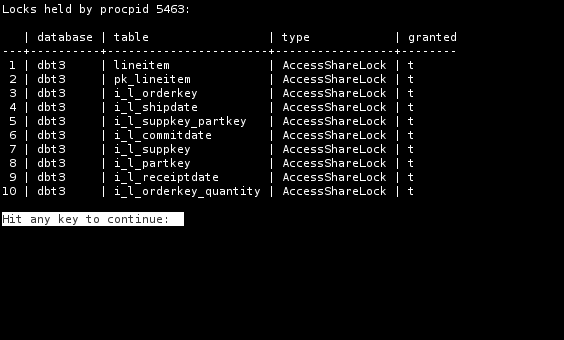
Lock Aquired
Use the ‘L’ key and enter a PID once pg_top is started.
Table Statistics
Use the ‘R’ key to display user table statistics. Use ‘t’ to toggle between displaying cumulative and differential statistics.
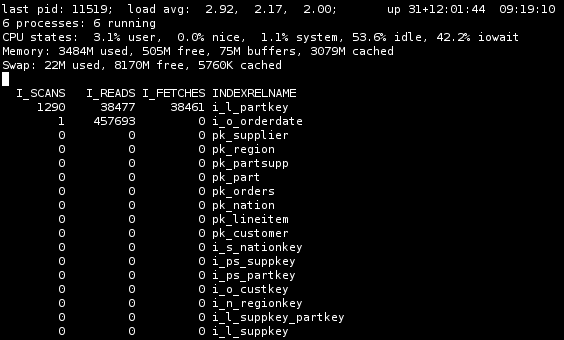
Index statistics
Use the ‘X’ key to display user index statistics. Use ‘t’ to toggle between displaying cumulative and differential statistics.
pg_activity
NAME
pg_activity - Realtime PostgreSQL database server monitoring tool
SYNOPSIS
pg_activity [-UphdC]
DESCRIPTION
pg_activity is a htop like application for PostgreSQL server activity
monitoring.
COMMAND-LINE OPTIONS
-U USERNAME, --username=USERNAME
Database user name (default: $USER).
-p PORT, --port=PORT
Database server port (default: "5432").
-h HOSTNAME, --host=HOSTNAME
Database server host or socket directory (default: "localhost").
-d DBNAME, --dbname=DBNAME
Database name to connect to (default: "postgres").
-C, --no-color
Disable color usage.
--help
Show this help message and exit.
--version
Show program's version number and exit.
ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
PGPASSWORD
PostgreSQL password
PGPASSFILE
Path to .pgpass file (default is ~/.pgpass)
DISPLAY OPTIONS
--no-database
Disable DATABASE.
--no-client
Disable CLIENT.
--no-cpu
Disable CPU%.
--no-mem
Disable MEM%.
--no-read
Disable READ/s.
--no-write
Disable WRITE/s.
--no-time
Disable TIME+.
--no-wait
Disable W.
INTERACTIVE COMMANDS
C Activate/deactivate colors.
r Sort by READ/s, descending.
w Sort by WRITE/s, descending.
c Sort by CPU%, descending.
m Sort by MEM%, descending.
t Sort by TIME+, descending.
Space Pause on/off.
v Change queries display mode: full, truncated, indented
UP / DOWN Scroll process list.
q Quit
+ Increase refresh time. Maximum value : 3s
- Decrease refesh time. Minimum Value : 1s
F1/1 Running queries monitoring.
F2/2 Waiting queries monitoring.
F3/3 Blocking queries monitoring.
h Help page.
R Refresh.
NAVIGATION MODE
UP Move up the cursor
DOWN Move down the cursor
k Cancel the backend
Space Back to activity
q Quit
EXAMPLES
PGPASSWORD='mypassword' pg_activity -U pgadmin -h 127.0.0.1 --no-client
-C
pg_activity -h /tmp
@see : http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/saucy/man1/pg_activity.1.html
You can also query the pg_stat_activity table of your database.
- http://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.2/static/monitoring-stats.html
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17654033/how-to-use-pg-stat-activity
- http://www.question-defense.com/2008/11/12/postgres-table-pg_stat_activity-table-fields-explained